How the Internet of Things (IoT) is revolutionising building energy efficiency
The UK Government is committed to reaching net zero by reducing greenhouse gas emissions by 100 percent from 1990 levels by 2050.
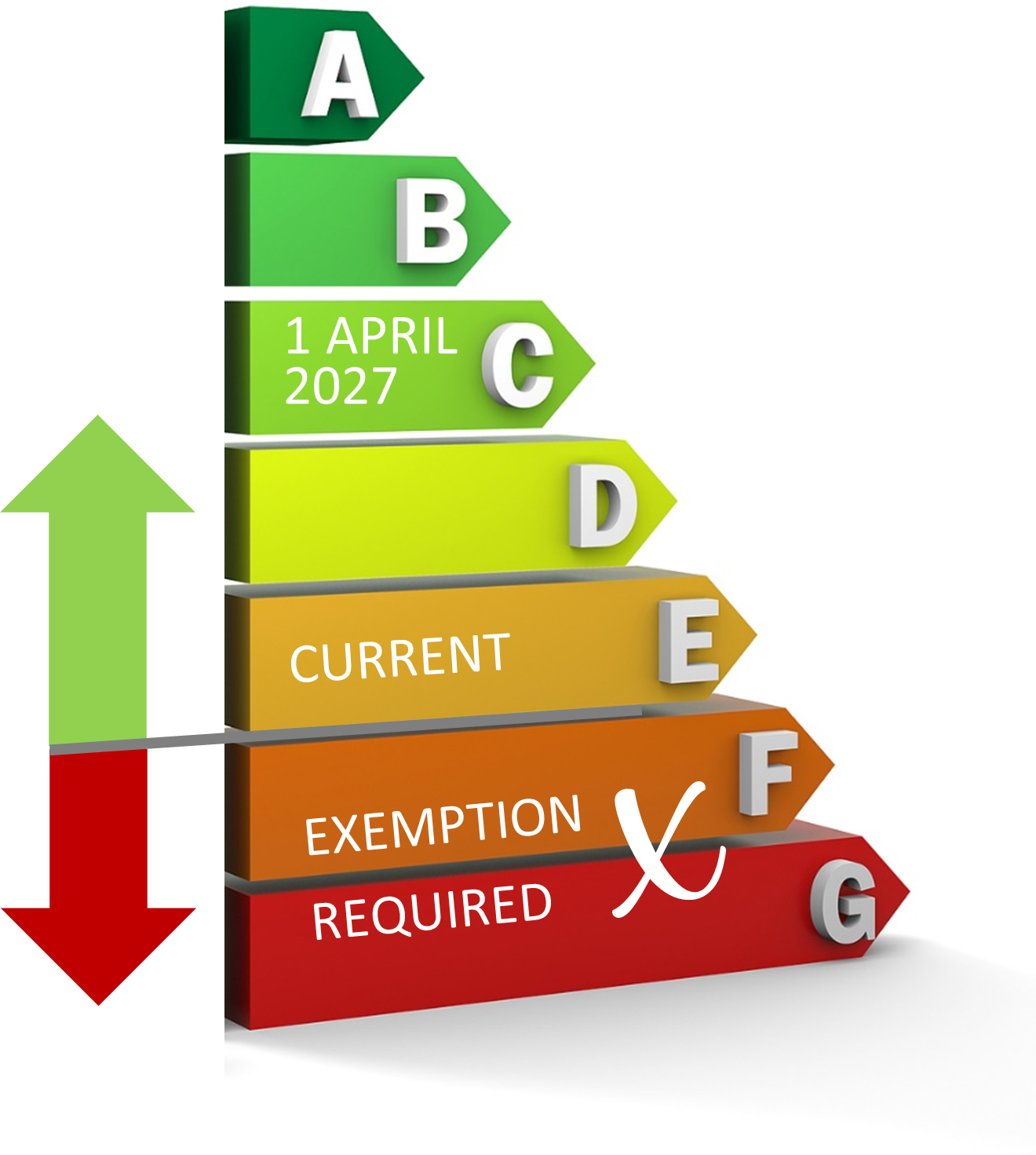 The built environment must therefore progress decarbonisation
urgently for a number of reasons, the first being that the Minimum Energy
Efficiency Standards (MEES) are now in force, and it is a legal requirement for
buildings to become increasingly energy efficient over the next few years. The
second, soaring energy prices, have brought building optimisation quickly up
the agenda for building owners and managers. And in addition, the demand for
green buildings is rising rapidly as found in the recent RICS Sustainability Report. The report found that occupier and investor
demand for green buildings is continuing to rise in the UK, with nearly half of
respondents reporting lower rents and sale prices for non-sustainable
buildings.
The built environment must therefore progress decarbonisation
urgently for a number of reasons, the first being that the Minimum Energy
Efficiency Standards (MEES) are now in force, and it is a legal requirement for
buildings to become increasingly energy efficient over the next few years. The
second, soaring energy prices, have brought building optimisation quickly up
the agenda for building owners and managers. And in addition, the demand for
green buildings is rising rapidly as found in the recent RICS Sustainability Report. The report found that occupier and investor
demand for green buildings is continuing to rise in the UK, with nearly half of
respondents reporting lower rents and sale prices for non-sustainable
buildings.
Buildings use around 40% of all global energy and emit approximately 30% of all greenhouse gases. It is therefore an obvious target for change when trying to drive down energy consumption and the resultant CO2 emissions.
However, the Internet of Things (IoT) is playing a vital role in addressing the global need for improved energy efficiency, revolutionising the way we interact with technology, connecting devices and enabling seamless communication between them. And one area where its impact is particularly evident is in the field of building energy management.
Smart
sensors and data analytics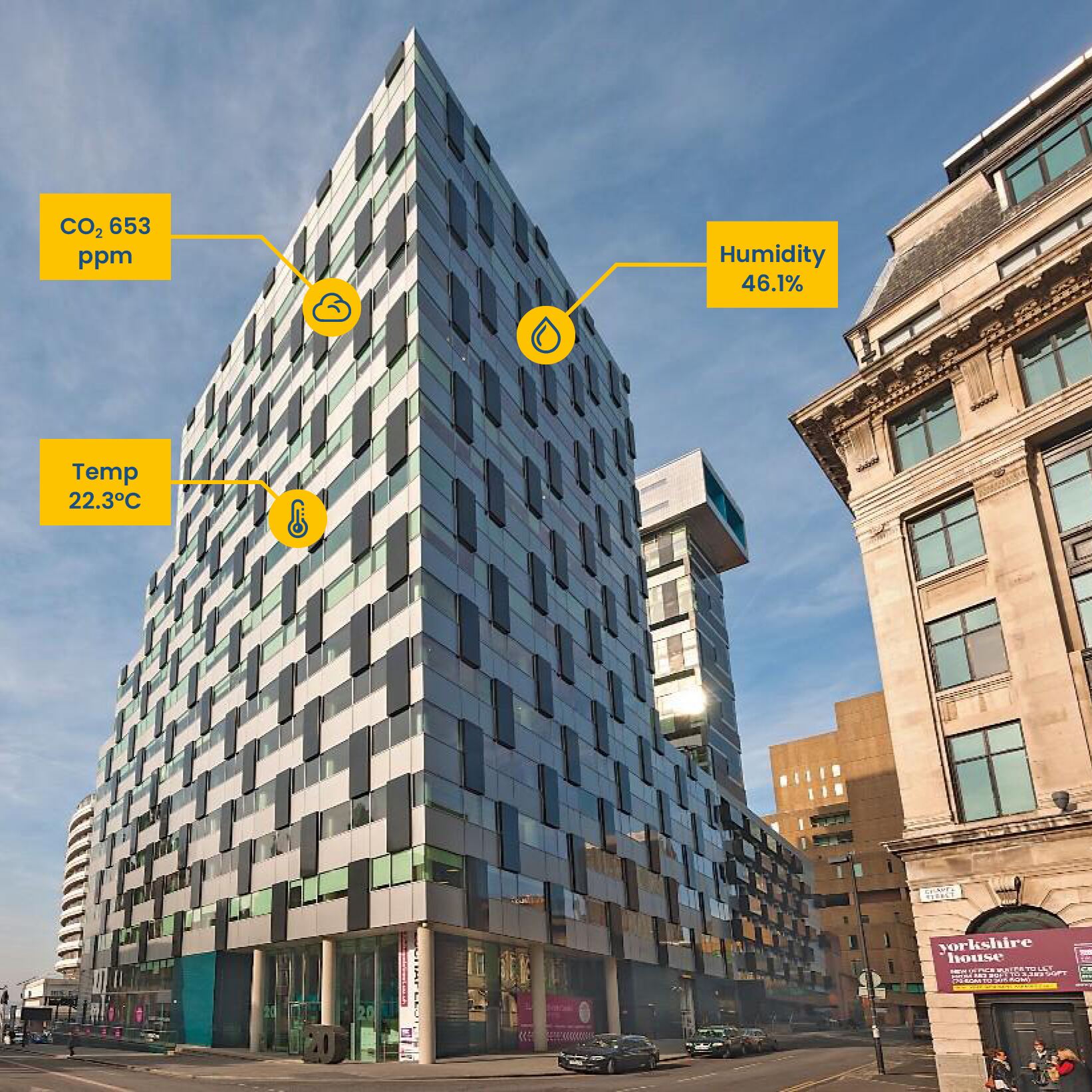
IoT-enabled sensors and devices are revolutionising the way buildings are monitored and managed. With a network of connected devices, building managers can collect real-time data on energy usage, temperature, occupancy, and other key parameters. This influx of data allows for a more granular understanding of a building's energy usage patterns, enabling precise optimisation. By monitoring these variables, building management systems can make informed decisions about adjusting heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems, lighting, and other energy-intensive equipment. Data analytics algorithms identify trends, inefficiencies, and potential areas for improvement, empowering building managers to implement targeted energy-saving measures.
Intelligent
HVAC systems
Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems account for a substantial portion of a building's energy consumption. However, IoT technology offers the ability to monitor and control these systems more efficiently. By integrating sensors and actuators, these systems can dynamically adjust temperature and airflow based on occupancy, temperature, weather conditions, and user preferences. Smart thermostats can learn from user behaviour and optimise heating and cooling schedules accordingly, preventing energy waste resulting from heating or cooling unoccupied spaces. These intelligent HVAC systems can lead to significant energy savings by avoiding unnecessary heating or cooling and therefore reducing overall energy consumption.
Intelligent
lighting systems
Lighting is another major energy consuming aspect of buildings, however, with IoT enabled lighting systems, energy waste can be substantially reduced. Smart lighting systems equipped with occupancy sensors automatically adjust illumination levels based on the presence or absence of people in a room. These systems can also be synchronised with natural daylight, dimming, or turning off lights when sufficient natural light is available. By dynamically controlling lighting, energy usage is optimised, and substantial energy savings can be made.
Energy
management and automation
IoT platforms provide building managers with centralised control and automation capabilities. These platforms allow for remote monitoring, control, and optimisation of various building systems, including lighting, HVAC, and energy management. By integrating data from multiple sources, building managers can gain comprehensive insights into energy usage and implement strategies to optimise efficiency. Automated systems can respond to real-time data and adjust operations accordingly, ensuring that energy is used effectively and only when needed.
Predictive
maintenance
IoT enabled sensors can also monitor the performance of various building systems and equipment, providing valuable data for predictive maintenance. Traditional maintenance practices in buildings often follow a fixed schedule or react to equipment failures, an approach that is not only inefficient but can also lead to energy wastage and downtime. IoT-enabled predictive maintenance solutions use real-time data and machine learning algorithms to identify potential issues before they escalate into major problems. By analysing real-time data and identifying potential issues before they escalate, building managers can proactively schedule maintenance activities, reducing downtime and improving the lifespan of equipment. This approach minimises energy wastage resulting from inefficient or malfunctioning systems, leading to improved energy efficiency and reduced maintenance costs.
 Overall, the Internet of Things is revolutionising building
energy efficiency by providing real-time monitoring, data analytics, and
intelligent automation capabilities. By harnessing the power of IoT devices and
systems, buildings can become smarter, more sustainable, and more energy
efficient. The integration of IoT technology enables building managers to
optimise energy consumption, reduce wastage, and lower operational costs. And,
as IoT continues to evolve, the potential for further advancements in building
energy efficiency is immense, contributing to a greener and more sustainable
future.
Overall, the Internet of Things is revolutionising building
energy efficiency by providing real-time monitoring, data analytics, and
intelligent automation capabilities. By harnessing the power of IoT devices and
systems, buildings can become smarter, more sustainable, and more energy
efficient. The integration of IoT technology enables building managers to
optimise energy consumption, reduce wastage, and lower operational costs. And,
as IoT continues to evolve, the potential for further advancements in building
energy efficiency is immense, contributing to a greener and more sustainable
future.
Latest Articles
Evotech sponsors BIG North Pole Sea Ice Research Expedition
Read More >Evotech expands its footprint with new London hub
Read More >Government launches Occupational Health Taskforce
Read More >200 schools in London to have air filters installed in classrooms
Read More >



